Heat pump installation or replacement: prices and information
Have you bought a new home and are you thinking about the best solution for your heating system? Have you opted for the installation of a heat pump as the central element of your system and are you looking for information on the types and characteristics of this variant? Or do you already have a heat pump at home and want to replace it due to malfunction or breakage of some of its components? You are in the right place, in this guide we will try to give you all the information you need to request a free quote from the best local HVAC pros in your area registered on LocalProBook.
Price table for heat pump
Do you want to renovate your home with a heat pump? Prices can be found in the table below, with indications also on supply and installation. The figures indicated are to be considered excluding the federal and state's TAX.
| Heat pump type - Prices per unit | Price from - to |
|---|---|
| Geothermal heat pump | $3400 - $6600 |
| Air-to-air heat pump | $2300 - $4600 |
| Air-to-water heat pump | $2900 - $5400 |
| Heat pump installation - Prices per unit * | Price from - to |
| Labor for turnkey installation | $3300 - $6500 |
NOTE that prices may vary according to the type of work to be carried out, the quality of its execution, and the region where you are.
What is a heat pump: different types
Are you evaluating the new heating system to install the heat pump at affordable prices? Are you fed up with the continuous maintenance required for the old boiler consumption is excessive, so would you like to replace it with a new heat pump?
If you are seriously considering requesting the installation of a new heat pump at prices that match your budget, don't underestimate the importance of contacting true professionals in this sector, in order to have a contact person who can provide you with the right advice, which you orient yourself on the best choices and who knows how to find solutions in line with your needs.
Our professionals will be able to offer you the possibility to choose between:
- Natural gas heat pump
- Air-to-air heat pump
- Water-to-water heat pump
- Reversible heat pump
- Packaged heat pump
The panorama of usable sources is very broad. For example, the air heat pump draws air from outside, the water heat pump draws it from water sources such as groundwater, rivers, lakes, or rainwater tanks ( additional permissions may be required ). The reversible heat pump, on the other hand, is able to provide heat in the winter and coolness in the summer. Finally, the monobloc heat pump is connected to the system via water pipes that reach inside the house.
How does a heat pump work?
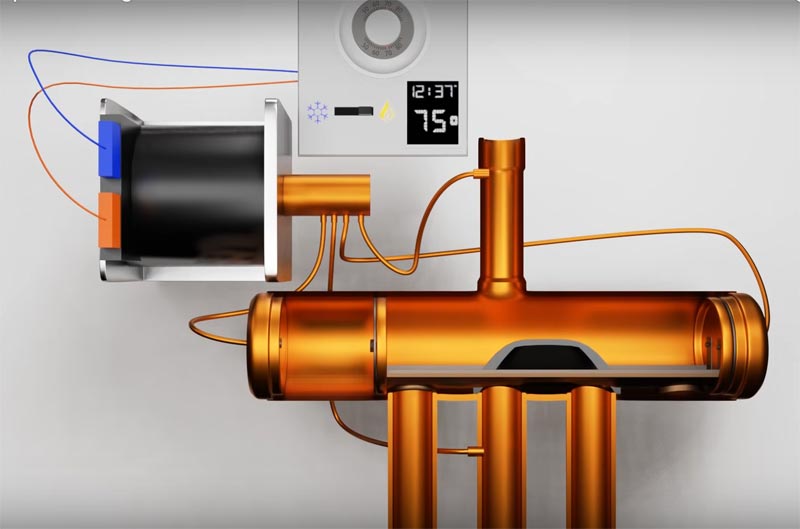
The operation of a heat pump is carried out through the use of a kind of closed circuit, which has some necessary elements to realize its ultimate goal. The main elements of the circuit are a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, evaporator, and, in addition, refrigerant, which is nothing but a liquid that can interact depending on the conditions in which it is, turning into a liquid or steam.
The refrigerant will thus have the following characteristics depending on whether it is handled by one path component or another:
- The compressor enters the gaseous state from the evaporator. As a result of compression, the pressure in it rises, and it heats up with a certain force.
- In the condenser, the refrigerant undergoes transformation, turning it into a liquid. At the same time, it loses heat to the outside, previously accumulated in the compression process.
- The passage of the liquid refrigerant through the expansion valve causes it to cool and partially convert to vapor.
- In the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs heat from outside and actually evaporates.
The components of a closed-loop heat pump can be assembled into a single unit, but it is also possible that they are divided into two parts, which are technically defined as split systems. Both systems are in any case connected by pipes containing refrigerant.
The two elements of the circuit called the condenser and the evaporator, are formed by tubes in which the refrigerant flows. These tubes have the technical name "heat exchangers" and are in contact with a working fluid formed by water or even air.
Summing up the operation procedure of a heat pump, we will have a compressor that gives energy to the refrigerant. Entering the evaporator, it absorbs heat from the environment and transfers it to the heated medium through the condenser.
Heat pump for heating: pros, cons, and differences with other systems
As with other heating systems, heat pumps also have pros and cons. One of the main advantages is environmental sustainability. In fact, the heat pump transfers heat thanks to a renewable and free energy source (air, water, or ground). In terms of environmental protection, it means significantly reducing CO2 emissions.
The heat pump is very efficient as it can produce more energy than needed. The exploitation of renewable sources translates into a great economic advantage, compared to heating costs. If reversible pumps are considered, it is also possible to obtain both heating and cooling, making the air conditioner unnecessary. The heat pump does not require the construction of flues.
Among the cons, there is the fact that the heat pump is not always the ideal solution. In fact, it requires the availability of heat sources (water, air, earth).
The heat pump requires a very large installation space compared to other heating systems. In addition, the heat pump, to work properly, requires certain temperatures that are not always reachable, based on the heat source it draws on.
If it is a pump that is also able to provide cooling instead, through the inversion of the cycle, the pump works with the same principle as the refrigerator at home.
The heat pump is also capable of producing domestic hot water, which is used in the bathroom and kitchen. The hot water is heated in storage tanks and distributed via hydraulic pipes.
The heat pump can integrate with radiators, fan coils, splits, and radiant panels.
How many square feet will a 1-2-3-4 ton heat pump heat?
- 500 - 700 square feet: 1 ton.
- 1,000 - 1,200 square feet: 2 tons.
- 1,500-1,800 square feet: 3 tons (3-ton is equal to 36,000 BTU).
- 2,000-2,2500 square feet: 4 tons.
Most installed heat pumps: 3 ton heat pump and 4 ton heat pump.
Why is a heat pump better than a gas furnace for heating my house?
Heat pumps and gas furnaces are both viable options for heating a house, but there are some reasons why a heat pump may be a better choice for some homeowners:
- Energy efficiency: Heat pumps are highly energy-efficient, using up to 60% less energy than traditional electric furnaces and up to 30% less energy than gas furnaces. This can result in significant cost savings on energy bills over time.
- Environmental impact: Heat pumps produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions than gas furnaces, making them a more environmentally friendly option.
- Versatility: Heat pumps can be used for both heating and cooling, making them a more versatile option than gas furnaces.
- Safety: Heat pumps do not produce carbon monoxide, which can be a safety concern with gas furnaces.
- Comfort: Heat pumps provide more consistent heating than gas furnaces, as they do not produce hot or cold spots in the home.
- Longevity: Heat pumps typically have a longer lifespan than gas furnaces, lasting up to 15 years or more with proper maintenance.
Which terminals to choose based on your needs

As mentioned, the heat pump works with different types of terminals, including:
- Cast iron radiators
- Steel radiators
- Aluminum radiators
- Underfloor heating
Radiators ( cast iron, steel, and aluminum radiators ) are the most used and are made up of modular elements, connected to each other and within which the thermal fluid flows.
Underfloor heating requires considerable initial costs for installation, however to the benefit of consumption which is considerably reduced compared to that envisaged for radiators which require very high temperatures.
Heat pump water heater
- A heat pump water heater for hot water allows you to heat water 3-4 times more efficiently than a conventional boiler.
- Cool the room in which they are installed FREE OF CHARGE (because cold air is a by-product of the heat pump).
- The payback period for heat pumps is 4-6 years, depending on the consumption of hot water (the more hot water you use, the faster the payback). The payback period does not include tax breaks.
This kind of energy recycling provides a minimum burden on the environment, as it recycles the generated heat.
Components of Heat Pump Water Heaters
Heat pump water heaters are a type of water heater that uses electricity to move heat from the surrounding air into the water tank, rather than generating heat directly. Here are the main components of a heat pump water heater:
- Compressor: The compressor is the main component of the heat pump system, and is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas to increase its temperature.
- Evaporator: The evaporator is a coil that is located inside the heat pump water heater, and is responsible for absorbing heat from the surrounding air.
- Condenser: The condenser is a coil that is located outside the heat pump water heater, and is responsible for releasing heat into the surrounding air.
- Refrigerant: The refrigerant is a gas that is used to transfer heat from the surrounding air into the water tank.
- Heat exchanger: The heat exchanger is a component that transfers heat from the refrigerant to the water in the tank.
- Control panel: The control panel is responsible for monitoring and controlling the operation of the heat pump water heater, including temperature settings and diagnostic functions.
- Water tank: The water tank is where the heated water is stored, and is typically made of steel or glass-lined steel.
Heat pump water heater - detailed cons and pros
Heat pump water heaters are a type of water heater that uses electricity to move heat from the surrounding air into the water tank, rather than generating heat directly. Here are some pros and cons of heat pump water heaters:
Pros:
- Energy efficiency: Heat pump water heaters are highly energy efficient, using up to 60% less energy than traditional electric water heaters. This can result in significant cost savings on energy bills over time.
- Environmental impact: Heat pump water heaters produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions than traditional electric water heaters, making them a more environmentally friendly option.
- Long lifespan: Heat pump water heaters typically have a longer lifespan than traditional electric water heaters, lasting up to 15 years or more with proper maintenance.
- Versatility: Heat pump water heaters can be used in a variety of settings, including homes, apartments, and commercial buildings.
Cons:
- Upfront cost: Heat pump water heaters are generally more expensive to purchase and install than traditional electric water heaters, which can be a barrier for some homeowners.
- Space requirements: Heat pump water heaters require a larger space than traditional electric water heaters, as they need to draw in air from the surrounding environment to operate.
- Noise: Heat pump water heaters can be noisy during operation, which can be a concern for some homeowners.
- Climate dependence: Heat pump water heaters are less efficient in colder climates, as they rely on the surrounding air to generate heat. In very cold climates, a backup heating system may be necessary.
Overall, heat pump water heaters can be a highly efficient and environmentally friendly option for heating water, but they may not be the best choice for every home or situation. It's important to consider the pros and cons carefully and consult with a licensed HVAC professional to determine if a heat pump water heater is the right choice for your specific needs and circumstances.
Heat pump for pool
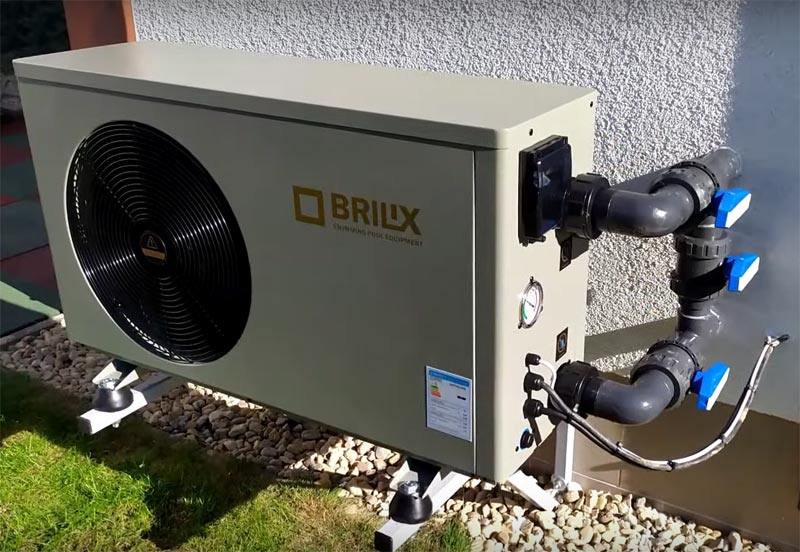

Heating the water in the pool makes it possible to visit it throughout the year and at the same time places a heavy financial burden on the owners, increasing costs. It is possible to reduce heating costs by 3-6 times by installing a pool heat pump. During the operation of the heat pump, for each kilowatt of electricity consumed, about 3-6 kW of heat is produced.
How to choose a heat pump for a pool
The performance of thermal stations allows the use of a heat pump to heat the water of a public and private pool. In order for the system not to fail, you will need to correctly calculate the power of the HP, select the model of a suitable manufacturer, and calculate how much it will cost to purchase and install the station.
Only according to preliminary calculations, the connection of HP to the pool will save so much money that in 3-5 heating seasons, the station will reach full self-sufficiency, of course, subject to the correct choice of installation.
Detailed pros and cons of heat pump for a pool.
Heat pumps are a popular option for heating swimming pools, as they are energy-efficient and can provide consistent heating throughout the swimming season. Here are some pros and cons of using a heat pump for a pool:
Pros:
- Energy efficiency: Heat pumps are highly energy-efficient, using up to 80% less energy than traditional pool heaters. This can result in significant cost savings on energy bills over time.
- Consistent heating: Heat pumps can provide consistent heating throughout the swimming season, regardless of the outside temperature. They can maintain a consistent water temperature, which can be more comfortable for swimmers.
- Environmentally friendly: Heat pumps produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions than traditional pool heaters, making them a more environmentally friendly option.
- Low maintenance: Heat pumps require minimal maintenance, as they have few moving parts and do not require regular cleaning or replacement of filters.
Cons:
- Upfront cost: Heat pumps are generally more expensive to purchase and install than traditional pool heaters, which can be a barrier for some pool owners.
- Climate dependence: Heat pumps are less efficient in colder climates, as they rely on the surrounding air to generate heat. In very cold climates, a backup heating system may be necessary.
- Space requirements: Heat pumps require a larger space than traditional pool heaters, as they need to draw in air from the surrounding environment to operate.
- Noise: Heat pumps can be noisy during operation, which can be a concern for some pool owners.
When should you replace a heat pump?
The heat pump has a very long life, especially if maintenance is carried out regularly. In some cases, however, there may be anomalies and malfunctions which may make it necessary to replace the system.
If you are facing home renovations, you can take the opportunity to replace the heat pump and take advantage of the tax deductions.
Heat pump maintenance regulations and obligations: how to avoid the most common problem
The heat pump, like other heating systems, is managed by a specific regulation, which indicates the guidelines for the management of the system itself. The legislation requires compliance with regular coupons or maintenance, to be recorded in a special system booklet, which represents the system's identity document.
In the booklet you can find all the characteristics of the system, namely:
- Plant code
- Fuel used
- Power
- Maintenance and efficiency reports
Heat pumps must undergo efficiency checks every 4 years and correct maintenance management allows you to benefit from your heat pump for a long time.
Heat pump: the recommended brands
European manufacturers of heat pumps
In general, it can be said that European brands are far superior to Asian ones. This is due to a clear difference in service centers, durability, and temperature optimization.
Some of the best brands include:
- Clima Veneta, which sells products suitable for all needs
- Viessmann, German, the world leader in heating systems
- Buderus is a trademark owned by Bosch Thermotechnik GmbH, which is part of Robert Bosch GmbH. Under this brand, components of heating systems for various types of buildings and structures are produced.
- Vaillant, German, which produces very efficient monobloc and compact solutions
- Daikin, the company witha German engine and specialized in hybrid systems
- Shüco, exceptional for domestic water heat pumps
- NIBE manufactures heating, cooling, ventilation, and energy-saving systems for residential buildings.
In addition to those listed, other brands are also on the market, such as Clivet, GREE, SANYO, Rossato Group, Mitsubishi, and Lovato; capable of guaranteeing high-level performance.
Heat pump manufacturers in the USA
- The company FHP (USA) has been manufacturing heat pumps for more than 30 years, being a recognized leader in the world market.
- Goodman. The main goal of the Goodman company is to produce high-quality products at an affordable price, as well as to protect products with one of the best guarantees in this field. This goal has established Goodman as a leading manufacturer of residential heating, commercial, and air conditioning equipment.
- Rheem Manufacturing Company is an American privately held manufacturer that manufactures domestic, and commercial water heaters and boilers, as well as heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) equipment. The company also manufactures and markets products under the brand name Ruud.
- ClimateMaster was born from the merger of several heat pump companies. For more than 50 years, ClimateMaster has been developing and implementing heat pumps.
- Mammoth Corporation in the production of climate technology focuses on the application in the development of systems to maximize the use of energy sources based on renewable, environmentally friendly, and safe technologies. Mammoth has been a member of the International Association of Geothermal Heat Pumps for many years.
- ECONAR is a company from Minnesota (USA), known for its cold winters. The company has been manufacturing heat pumps for over 20 years. Among the consumers of its products: private households, churches, banks, schools, car washes, swimming pools, restaurants and other places where heat and hot water are needed.
- Enertech Manufacturing - Manufactures geothermal heating and cooling systems under the GeoComfort and Hydron Module brands for commercial and private sectors.
- Hydron Module is a manufacturer of geothermal heating and cooling systems.
- Lennox International Inc. is a supplier of equipment for external climate control systems. Lennox manufactures and markets a wide range of products related to heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration systems.
Heat pump: tax deductions and energy label
If households take steps to reduce their carbon footprint, they could soon be able to claim thousands of dollars in tax credits and benefits.
The Inflation Reduction Act, which President Joe Biden signed into law on August 16, represents the largest federal climate change investment in US history. Among other measures, the law provides financial incentives for consumers who, for example, buy high-efficiency appliances, buy electric cars, or install rooftop solar panels or heat pumps.
It is worth noting that these incentives and different eligibility requirements take effect at different times.
When can I get tax credits to improve the efficiency of my home?
There are two tax credits for homeowners who make some upgrades:
- The "Non-Commercial Energy Property Loan" is a 30% tax credit of $1,200 per year. For example, it helps cover the cost of installing energy-efficient skylights, insulation, exterior doors, and windows. Annual limit - $2,000 - for heat pumps, heat pump water heaters, stoves, and biomass boilers.
- The Residential Clean Energy Credit is also a 30% tax credit. This refers to the installation of solar panels or other equipment using renewable energy sources such as wind, geothermal, and biomass fuels.
Tax incentives cover the cost of the project and are applied in the year the project ends. From a legal point of view, a project is completed when it is "commissioned".
The Clean Energy Extended Home Credit is retroactive from early 2022. Therefore, the installation of solar panels and other related projects completed between January 1, 2022, and the end of 2032 are eligible for a 30% loan. Those ending in 2033 and 2034, respectively, are entitled to 26% and 22%.
The Extended Non-Commercial Energy Asset Credit is available for projects completed after January 1, 2023, through the end of 2033. There are exceptions, for example, oil-fired stoves and hot water boilers with certain efficiency ratings only qualify until 2027.
"If you complete and install the project in 2022, it will not qualify for new stimulus," Ben Evans, federal legislative director for the U.S. Green Building Council, said of the secondary energy asset loan. "Look ahead and start planning projects because some of them will take time to complete."
One caveat: Because these are tax credits, consumers will only receive financial benefits when they file their annual tax returns.